Unemployment benefits can be a vital support for those experiencing unexpected job loss. If you received unemployment compensation for the first time in 2024, you may be wondering how it will impact your taxes. Since unemployment income is taxable at the federal level, it’s important to understand the process and the information you’ll need when filing your taxes. Let’s review the basics.
At a glance:
- Unemployment payments are taxable at the federal level.
- State taxation of unemployment benefits varies by state.
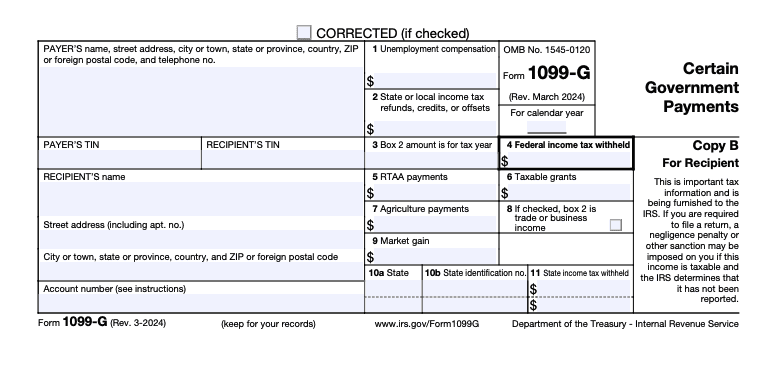
- Form 1099-G details all the unemployment compensation taxpayers received during the year and any federal or state taxes withheld.
Special considerations
Tax credits
If you received unemployment income this year, it could mean your income was less than in prior years. A lower income might make you eligible for tax credits you otherwise would not have been able to claim, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit.
Unemployment withholding
Also, keep in mind that if you didn’t have enough tax withheld from your unemployment benefits, you should expect to owe more at tax time. The opposite is also true — if you overpay taxes on your unemployment income, you’ll receive any excess money back as a tax refund.
How do I report my unemployment income in TaxAct?
If you use TaxAct® to file your federal tax return, reporting unemployment income is straightforward. We’ll walk you through the necessary steps and help you report your unemployment income correctly using our tax software.
To report this information using TaxAct:
- From within your TaxAct return (Online or Desktop), click Federal. (On smaller devices, click in the top left corner of your screen, then click Federal).
- Click the Other Income dropdown, then click Unemployment compensation.
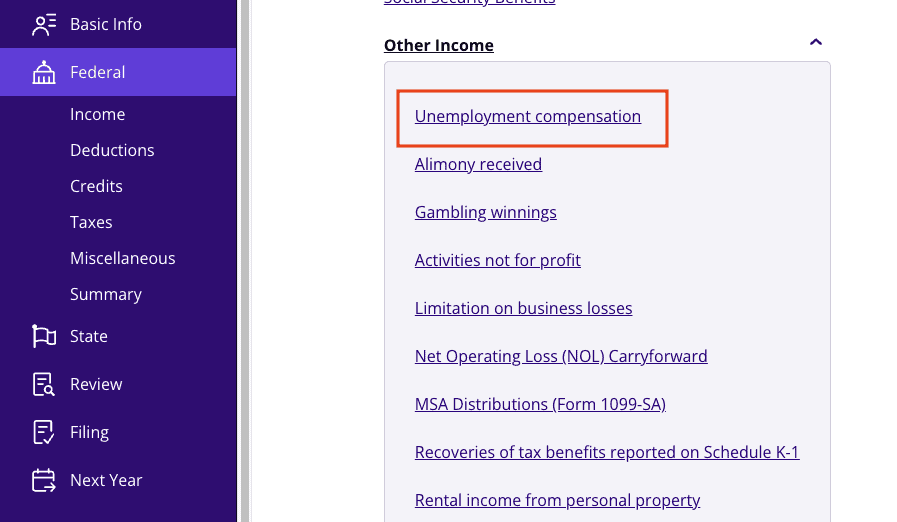
3. Click + Add Form 1099-G Unemployment to create a new copy of the form or click Edit to edit a form already created. (Desktop program: click Review instead of Edit).
4. Continue with the interview process to enter your information.
The bottom line
While unemployment benefits can provide crucial financial support during times of job loss, it’s important to understand their tax implications. Unemployment compensation is taxable at the federal level, and depending on your state, you may also owe state taxes.
By keeping track of your unemployment income through Form 1099-G and opting for voluntary tax withholding, you can make the tax process easier when filing your return. Remember to consult with your state’s tax agency for any specific guidelines, and be mindful of potential tax credits that may apply to your situation.